3D printers
- 3D printers for everyone
- 3D printers of all technologies (FDM, SLA, SLS, DLP, SLM)
- From entry-level to industrial 3D printers
- 3D printing of plastics and metal
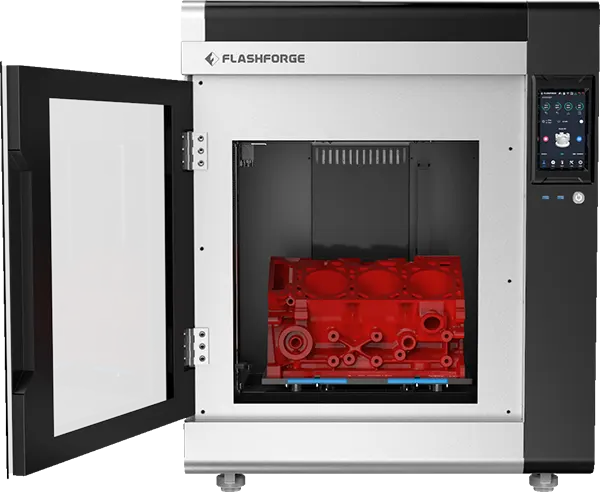

MORE ABOUT 3D PRINTERS
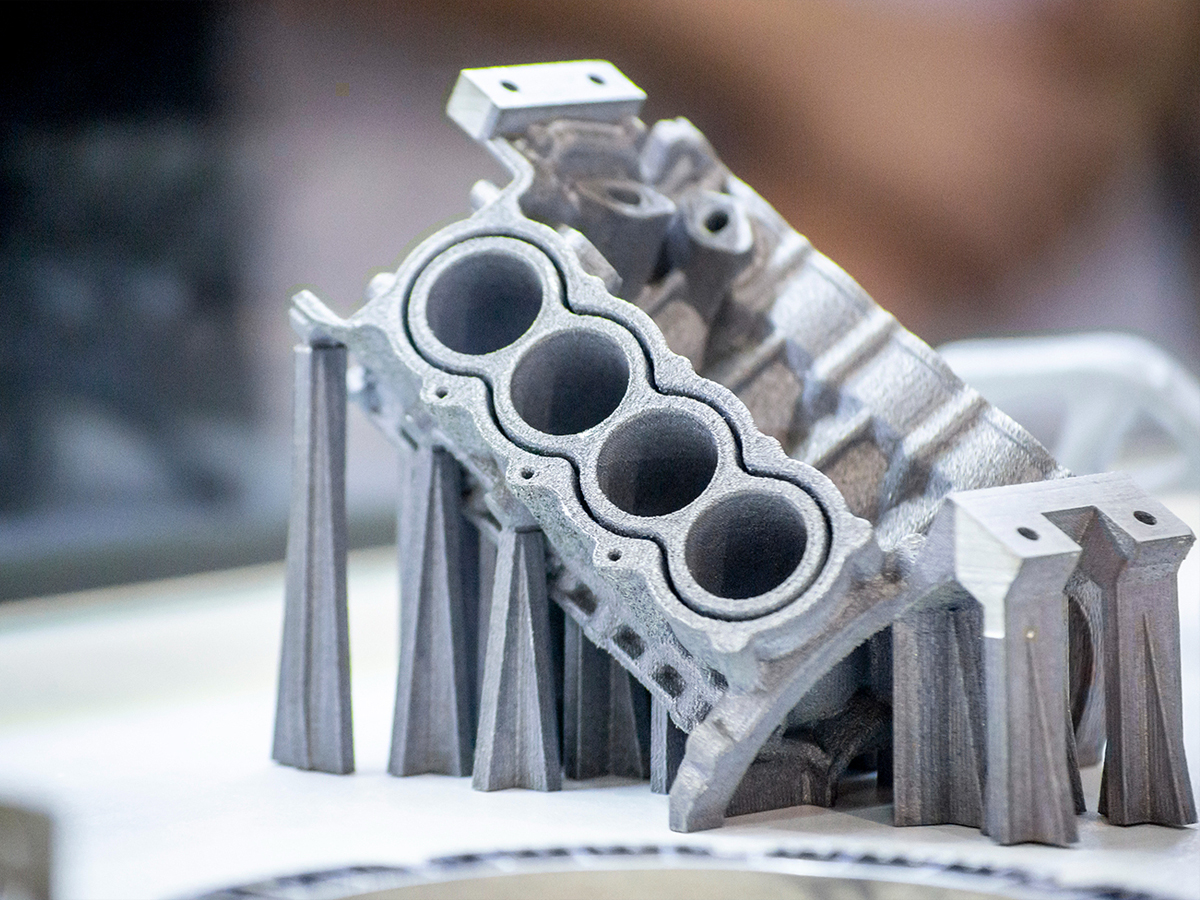
3D printing is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital (CAD) model. 3D printing makes it possible to create extremely complex shapes. It is an additive process in which layers of material are deposited sequentially in different forms. This is different from traditional production techniques, which involve removing material by methods such as cutting or drilling (subtraction processes).
3D printers typically perform 3D printing processes using digital technologies. Since the beginning of the 21st. For centuries, sales of 3D printers have increased sharply, while their price has fallen sharply.
3D printing technology is used for rapid prototyping and production of various products or semi-finished products in the fields of jewellery, footwear, industrial design, architecture, engineering and construction (AEC), automotive, aerospace, dental and medical, education, geographic information systems, civil engineering, etc.
3D printers can use many different materials for 3D printing (e.g. rubber, plastic, powder, resin, polyurethane materials, metals, etc.) and the choice depends on the capacity and type. In general, materials are applied layer by layer in a variety of ways, the most common of which is the application of a molten polymer through a small nozzle.
The polymer is in most cases a moulded plastic with favourable melting and cooling properties (in English, PLA bioplastics or the more durable ABS are used, which require a heated surface for application). 3D printers draw filament into a heated head (extruder) where it melts and is then applied to a working substrate or printed substrate (raft) through a nozzle.
Medicine
Dental
Consumer products
Education

The purpose of 3D printers
- production of complex parts
- rapid prototyping
- rare nerve parts
- jigs and fixings
- product customisation
- medical devices
- household products
THE MAIN BENEFITS OF HAVING A 3D PRINTER
Speed and simplification of the production process:
The main advantage of additive manufacturing. Complex parts and designs can be sprinted faster than those produced by conventional manufacturing. Most parts in the traditional manufacturing process require many steps, but in 3D printing, CAD models are loaded directly into the 3D printer and produced in a matter of hours. This helps you turn ideas into reality faster.
Design freedom:
3D printing is not affected by the constraints of conventional manufacturing, as the components are made layer by layer. So you can sprint all you want.
No waste material and no tension in the piece:
The extraction treatment produces waste material which is then discarded. In 3D printing, however, material is added, which significantly reduces waste and material procurement costs. Subsequent welding often causes additional stresses in the piece, whereas 3D printing does not.
FAQ - 3D PRINTERS AND 3D PRINTING
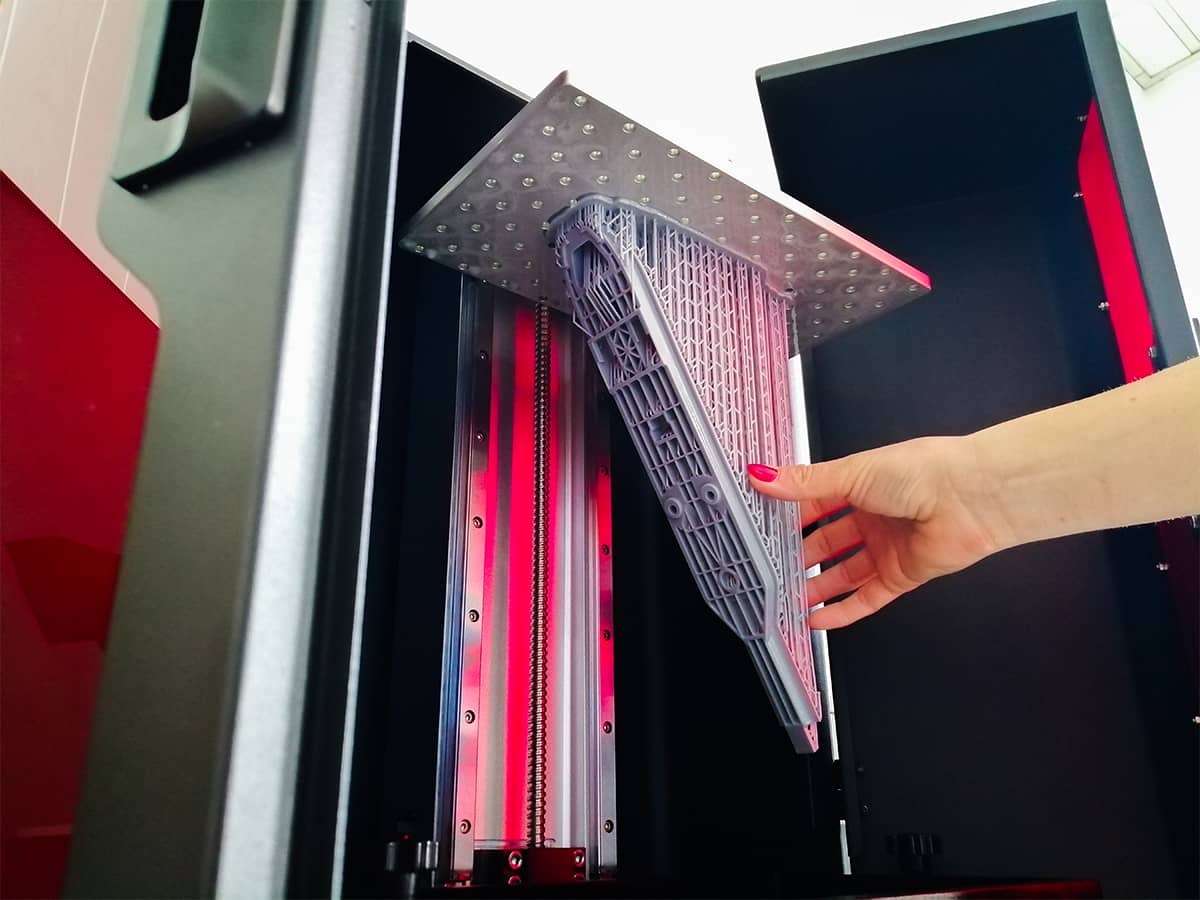

3D printing is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital (CAD) model. It enables efficient and rapid creation of exceptionally complex shapes. It is an additive process in which layers of material are sequentially deposited in various forms, distinguishing it from traditional manufacturing techniques that involve material removal methods.
3D printing offers numerous solutions in various fields. The applications of 3D printing are extensive due to few limitations:
- Prototyping: rapid production of a real piece from a CAD model.
- Manufacturing functional 3D parts: functional components with exceptional mechanical properties.
- Medicine: production of prosthetics, implants, and even organs.
- Art and design: crafting unique objects.
- Education: learning about 3D technology.
- Aerospace industry: manufacturing lightweight and rare components.
- Automotive industry: production of spare parts, molds, prototypes.
When entering the world of 3D printing, sooner or later you start thinking about which filament you need for 3D printing. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
PLA (Polylactic Acid): a biodegradable material of plant origin. It has minimal requirements and is easy for 3D printing. Compatible with a wide range of 3D printers.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): excellent mechanical properties – resistant to higher temperatures and UV light.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): a blend of PLA and ABS filament. The ideal combination of strength and flexibility. Good mechanical properties.
Buying a 3D printer can make many tasks easier for you, but you need to ask yourself several questions beforehand to find the right 3D printer for you:
- Needs and goals
- Type of 3D printer
- 3D printing volume
- Compatible materials (what products will you be printing?)
- Prior knowledge
- Budget
You can learn more about the steps before buying a 3D printer here.
Here are the most widespread 3D printing technologies:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): the most popular 3D printing technology, where the 3D printer deposits filament layer by layer through a nozzle.
- Stereolithography (SLA): uses a laser to solidify liquid resin.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): uses a laser to sinter powder material.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): uses a light projector to solidify liquid resin.
- Material Jetting (MJ): uses jetting print heads to spray liquid photopolymers onto a build platform layer by layer to create an object.
- Direct Energy Deposition (DED): uses a directed energy source (such as a laser or electron beam) to melt and deposit material.
All 3D printing technologies have their advantages and limitations.