3D printing technologies
Different 3D printing technologies provide solutions for many applications. Whether it’s home gadgets, complex engineering parts, prototypes or small batch pieces – the possibilities of 3D printing are almost endless, thanks in part to the many technologies available. Thanks to the deposition of layers of material, virtually any shape of object can be produced.
The advantage of 3D printing is the direct production of products from a CAD model without the use of moulds or tools. This is an additive process where successive layers of material are deposited. This is the quickest and most affordable way to get physical models. In 3D printing, there is significantly less waste material due to loading, not unloading.

THE MOST COMMON 3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGIES...
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling),
- SLA (Stereolithography),
- DLP (Digital Light Process),
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering),
- SLM (Selective Laser Melting),
- MJ (Material Jetting),
- DED (Directed Energy Deposition),
- LOM (Laminated Object Manufacturing)
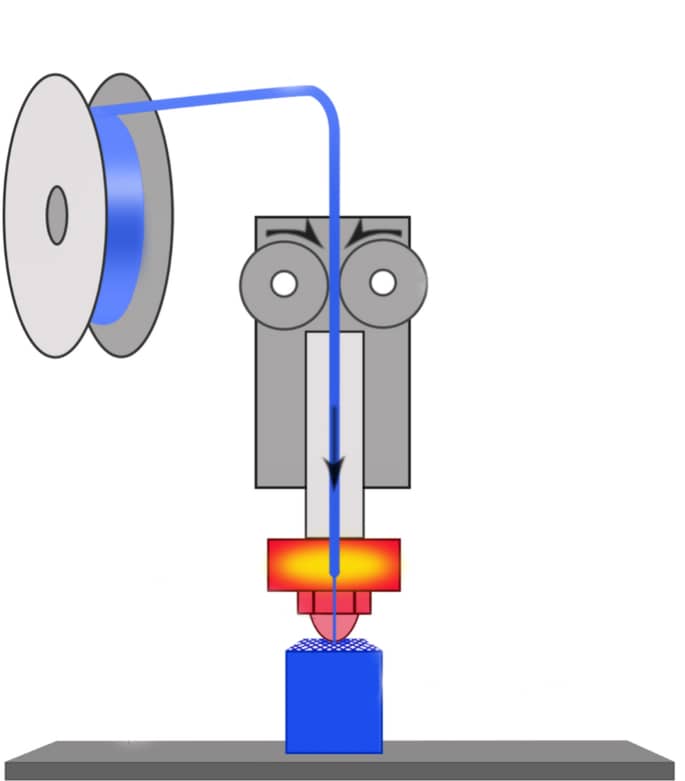
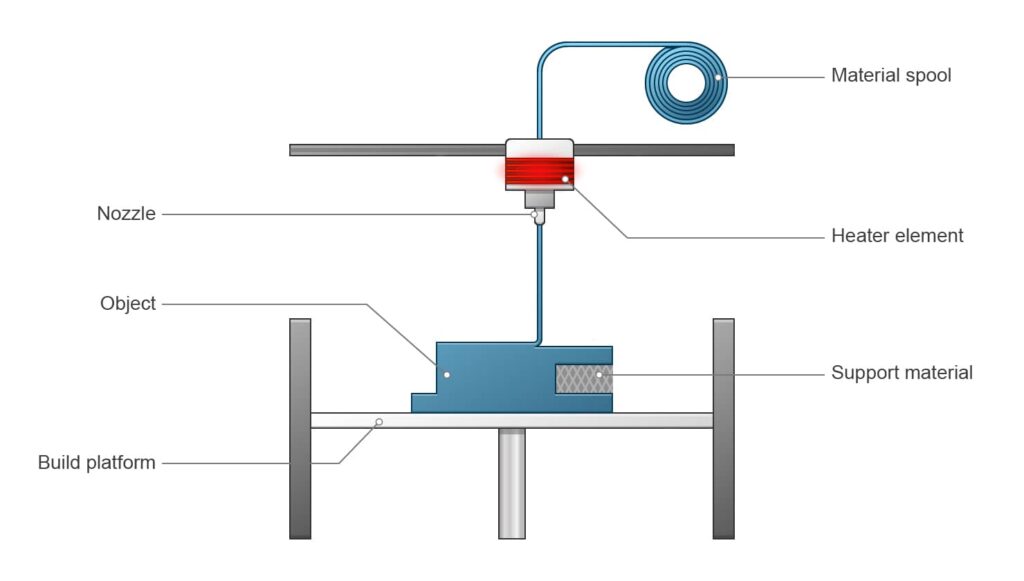
1. FDM – FUSED DEPOSITION MODELLING
The most widely used 3D printing technology for a wide range of users. The 3D printer draws the filament into the extruder, where it melts it and applies it to the work surface via a nozzle. There it cools and hardens. Programmed and precise movements of the head produce the final product.
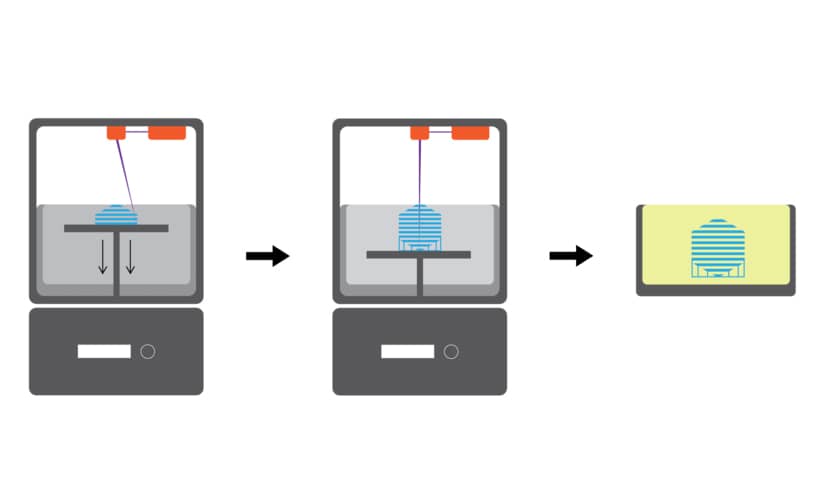
2. PHOTOPOLYMERISATION (SLA & DLP)
The most common are SLA (Stereolithography), the first in history, and DLP (Digital Light Processing). SLA is a slightly more precise method, using a laser to work in a more spot-like manner, making it more suitable for making smaller pieces. The light source penetrates the resin container by means of mirrors on the X and Y axes, which selectively cure the resin layer by layer. DLP 3D printing technology, on the other hand, uses a projector that has a wider beam of light. The piece is produced faster, but not with the same precision, so this method is used to produce larger pieces. Both technologies are widely used in dentistry and goldsmithing.
3. LASER TECHNOLOGY (SLS & SLM)
Laser 3D printing technology uses powder, which is applied layer by layer by laser, as the “building” material. When exposed to the beam, the temperature of the powder rises above the crystallisation temperature, which fuses the layers together. There are two laser technologies, SLS (Selective Laser Sintering), which is designed for printing plastic pieces, and SLM (Selective Laser Melting), which enables 3D printing of metal pieces.
4. MJ – MATERIAL JETTING
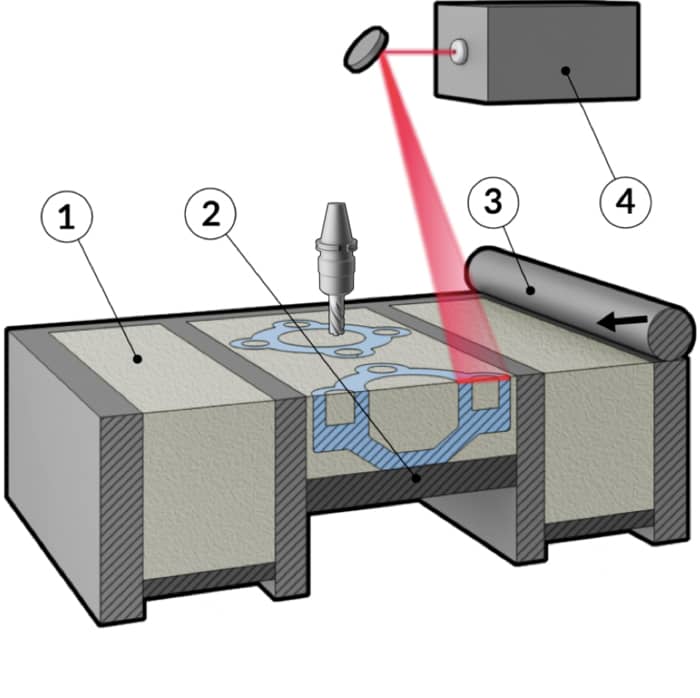
5. DED – DIRECT ENERGY DEPOSITION
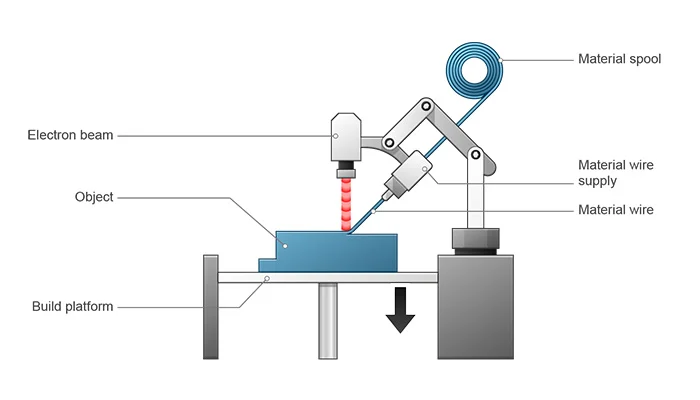
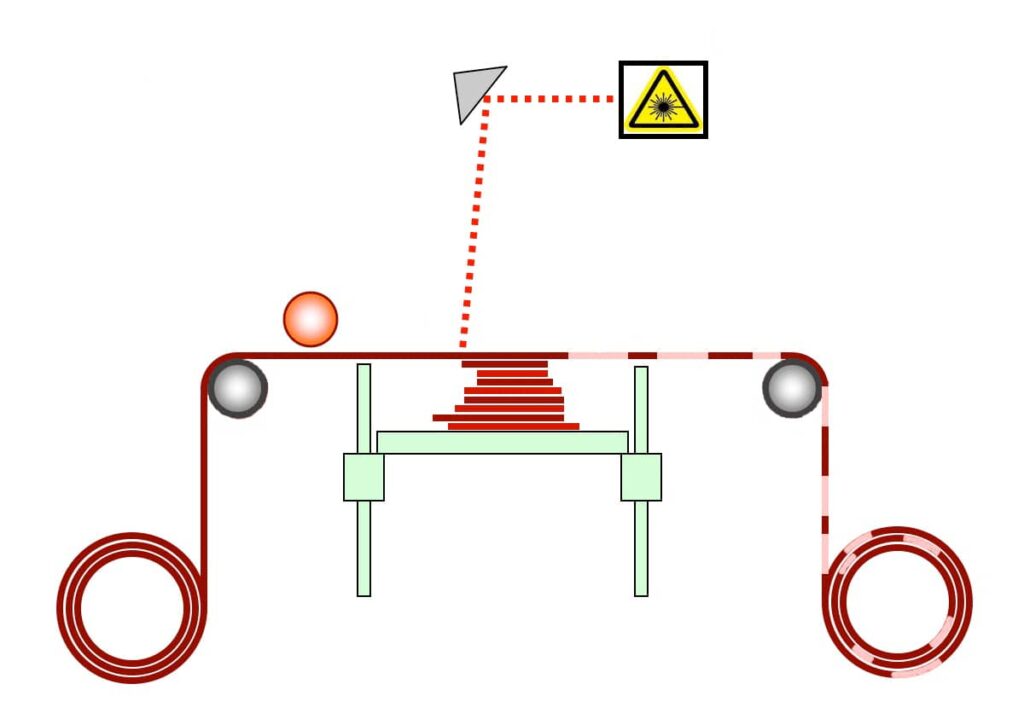
6. LOM – LAMINATED OBJECT MANUFACTURING
DIFFERENT 3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGIES FOR DIFFERENT NEEDS
Within their limitations, all of these 3D printing technologies offer a wide range of advanced solutions. 3D printing is evolving rapidly and provides users with efficient solutions.
The biggest benefits and advantages of 3D printing:
- Fast production time and low cost to develop an idea,
- Troubleshooting errors in the early stages of product development,
- Verification of dimensional suitability, form, functionality and ergonomics,
- Product optimisation before tooling.



